The white black
Regardless of our skin colour, we are all...Africans, literally
Genetics has disproven past prejudices concerning the inferiority or superiority of one race over another based on their differences. The term "race" was often misused when we did not know that all people were actually blood brothers. Science has proven that to us. What is left for us to do is to accept this not only in our minds, but also in our hearts, and stop mistreating each other, based on skin colour. Let us enjoy our differences. Our world is wonderful, because it is colourful.
Wayne Joseph- a 51-year-old Afro-American is a highly respected member of his community. Although he has suffered because of his dark skin, he is still proud of his origin. He names his daughter Kenya. He brings up his children not to be ashamed of being Afro-American. And because of his keen interest in the history of his family and their ancestral home Africa, Mr. Joseph runs a DNA test in order to obtain more information about his family roots on the Black continent. The results amaze him. The test reveals a huge European heritage and 0% African one. Zero! It almost turns out, that Mr. Joseph is not black, despite of his skin color.*
THE BULGARIAN AFRICAN
Evgeny Delev is a physicist engineer, a Bulgarian immigrant who has settled comfortably in France. His hobby is genetic genealogy. He is conducting the so-called Bulgarian genetic project.
Its goal is to convince as many of our fellow-countrymen as possible to run a DNA test and to provide their personal information to a common data bank, in order for a detailed genetic profile of the Bulgarian nation to be formed. Evgeny is an attractive man with extremely white face and auburn hair. Of course, one of the first things he did at the start of the project was to send his own biological material for a DNA analysis. The result: on the maternal side he is a pure...African.
He belongs to a group typical for the Black continent, which besides there, can be seen in the Middle East, among some tribes on the Arabian Peninsula and, naturally, among Afro-Americans.
However, it is a rare exception in Europe- apart from Evgeny, there are only 4 or 5 such known cases. What is the explanation? How is it possible for a person with "European genes" to be black and a person with African ones- to be white? Why have the races "mixed up"?
A DROP OF BLOOD
The term "race" originated as an attempt to somehow classify people with visibly different physical features such as skin colour, eye shape, etc. Even at its beginnings, this term was loaded with prejudice, because to the physical differences, people attached various presumptions concerning the person's qualities and abilities. One of the first to have made an attempt for such a classification is the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the XVIII century. He divides the human kind into 4 continental subtypes- Europeans, Asians, Americans and Africans.
He wrote: "Europeans are keen of mind, noble, inventive, law-abiding citizens. Africans are sly, lazy, negligent, succumbing to the whims of their masters". Encouraged by such "science", humanity has witnessed colonial exploitation, Indian genocide, trade with African slaves, Nazi (and not only) racism, holocaust, apartheid, Ku-Klux-Klan, the murder of Martin Luther King and so on. Until not long ago, the rule about the "one drop of blood" was valid in the US. According to that rule, children born within the marriage of a white person with a coloured one were considered coloured, regardless of how much that drop of blood has been diluted over the generations. This rule had various negative implications. It all started from a single misconception, which first appeared at the end of XVIII century- that different races did not have a mutual ancestor, but that each had emerged and had evolved separately on its respective continent. Moreover, it was believed that they did so at a different pace and with different "success". Therefore, you see, some were better than others.
With the above-said we can more or less summarize this view, known as polygenism. Ever since the middle of XX century, no self-respecting scientist has supported this view. It was rooted out by the genetics discovery that the whole humanity shared a mutual and recent origin. Only the Chinese, up until recently, still argued that the yellow race had originated separately from the rest- from the so-called Peking Man- a local East-Asian version of the predecessor of Homo sapiens. DNA analysis of people from East Asia has proven otherwise. Asians, as well as everybody else, also originate from Africa.
The second misconception at the core of racism is that one's abilities are defined only by their genetic heritage and that whatever environment they might be in, they would still be who they were born to be. The discussion, whether genes or social conditions define one's abilities, has never fully abated, but instead of furiously confronting each other, scientists are starting to agree more and more that both factors have to be taken into count in correlation instead of opposition.

The direct maternal line of Evgeny Delev proves, that round 12 000 years ago a greatgrandmother of his had lived in Africa
GENES DO NOT MAKE THE RACE
From the point of view of genetics, the term race is void of meaning. People look differently, but not because genetically they are completely different. It is exactly the opposite - we extremely similar, the degree of similarity between all human creatures on the planet is 99.9%.
We are the most unified species on the planet. In all other species the inter-species variety is much higher; even in the species closest to us - the chimpanzee; it is 3 times bigger than that of people.
Regardless of which race two people belong to, their DNA subsequence is 99.6% identical. The "Human genome" project came to the following conclusions regarding races:
1. Within members of a race, different from ours, we can always find an individual with whom we have a higher genetic similarity, than with someone from our race. 2. The genetic variations within a single race are much greater those between races. 3. Within the framework of one race there are some common genetic patterns. But there is no pattern, which is present in every single member of that group; there are also none that cannot be observed in representatives of another race. Furthermore, as James Watson wrote in his remarkable book "DNA- the secret of life", 98% of our variations fall in the section of the genome where they have no effect.
Moreover, since natural selection eliminates mutations which affect the functions of important parts of the genome extremely efficiently..., variations mostly accumulate in the non-coding sections. The differences between us are small, and the differences which those differences lead to, are even more inconsequential." The above-said leads to the conclusion that cannot be separated into races based on their genes. According to contemporary science, our apparent physical differences, which we call racial, are a relatively small number; they are also superficial as they are result from insignificant genetic factors. Furthermore, these factors in no way influence intelligence, talents or character.
BLOOD BROTHERS
We have already stated that as a species, people are surprisingly similar. That is because our common ancestor lived in Africa. From this point of view we are all African. Furthermore, he lived relatively soon- around 150 000 years ago. These 1500 centuries are a mere blink of the eye from the point of view of evolution- extremely insufficient, for many significant mutations to take place and for the human population to "break down" to different subspecies. We are all Homo sapiens sapiens regardless of our skin colour.
Then why do we look so different?
It is obvious that a black and a white person do not look alike. The difference is mostly on the outside- if they could 'take off' their skin, there would be no way for you to tell who was who. Other information is also needed.
THE NAKED MONKEY
Skin colour is the most apparent difference. But before we take a closer look at it, let us rewind evolution until the moment when the first human line separated from the one of the anthropoid apes. This took place 5 million years ago. For all this time, the accumulated difference in the DNA between the human and the chimpanzee- our evolutionarily closest relative, is only 1 %. If you shaved a chimpanzee, you would see that its skin is white. But the chimp is not bare-skinned; it has a thick dark fur, which, apart from other functions, protects it from the ultraviolet rays of the strong sunlight in the areas it populates. There is an interesting theory why, given the fact that we are so close with chimps, they are hairy, and we are not.
The human evolves as a species in an era much hotter than the current one.
The chimpanzee is a forest animal while the human first evolves in the savannah, where they cannot escape from the heat in the shades between trees. A thinner fur means easier cooling of the body. Therefore, the less hairy ancient humans were probably also healthier. Also, the more naked females were perceived as more attractive by the males and therefore had more children, thus passing on the "naked" gene to the next generations. The British zoologist Desmond Morris, who describes our species as a zoological phenomenon, calls the human a "naked monkey"; according to him, nudity is the most distinctive feature, which distinguishes us from all other primates. A light skin without fur is, however, very vulnerable to the harmful ultraviolet radiation of the Sun. Everybody who has had severe sunburn on the beach knows that. The harmful effects of the ultraviolet radiation are mitigated by melanin- a colouring pigment, produced in the skin. The genetic mutation, which led to an increased production of that pigment, has secured the survival of its carriers.
With time, this mutation became dominant in the human population inhabiting East Africa.

CAFE AU LAIT
However, around 80-60 000 years ago people started migrating. Some settled in Equatorial Africa, where the Sun is even stronger, and therefore their skin became darker. Even today the people who live there have the darkest skin. Others left the continent and headed towards South Asia and Australia.
In South India, where the Sun is still beating down rather hard, the skin remained dark- not completely black, but rather a shade of "cafe au lait".
But in the north it gets lighter and lighter. As to the ones who settled in Europe, their skin became completely white, because there the sun is weaker, and accordingly, so are the ultraviolet rays. Yet, they are necessary for the synthesizing of vitamin D, which is formed in the skin and is essential for calcium absorption. It is crucially important because it guarantees strong bones. Its chronic deficit leads to heavy skeleton deformations. In women, they can be so severe that they could render normal birth impossible. To put it in simply - you do not have Vitamin D, you do not have calcium and you do not have children. In order for the skin to be more permeable to the scarce sunlight, the melanin in it should be less, i.e. the skin should be lighter. This is how having a lighter skin tone ensures better survival chances in areas with limited sunlight. Why are Inuit, who live so far in the north, dark-skinned hen? Because they have found another way to adapt to their environment in order to receive sufficient quantities of vitamin D- they eat mainly fish, which contains the vitamin in abundance.
Europeans are not an "upgraded version" of Africans. If a few white-skinned families and their fair-haired children settled in Africa for 100 000 years, natural selection would have enough time to do what it is supposed to. What would happen? Probably a part of the children would not survive, developing skin cancer. The rest would have a generation. A mutation would occur in some of their descendents, which would cause an increase in melanin levels in the skin and it would get darker, because it is "healthier". In this way after a sufficient number of years has passed, the children of their children would all be dark-skinned.
WHITE MEN CAN JUMP
Beside the fact that after people inhabited Europe they got whiter, their bodies changed as well. Why? In the heat of Africa, where the body should easily cool itself, there developed two body types with optimal ratio between skin surface and volume. The first one- the tall and skinny Maasai, are characterised by a constitution allowing body heat to be easily released. In the other one- the Pygmies, the body changed in such a way as to minimize energy expenditure when moving. They are hunters who are always on the run. In order to save energy their bodies got smaller; fewer calories were needed for their maintenance and they did not feel as heavy during the constant sprint under the beating sun. In the significantly colder Europe, which went through an Ice Age even after it was inhabited by people, the body should retain as much body heat as possible. Therefore, it became stockier with less skin surface, through which the heat could escape, and with a more massive bone system. Because of the differences in body structure, some claim that the best contestants in weight lifting are European, and the fastest athletes- African. But within each race there are various body constitutions.
Take the best high-jump athlete - the slender and long-legged Stefka Kostadinova, for example. Who says that white people cannot jump? Races differ in teeth structure, serum proteins, the percentage distribution of blood groups, type of colour-blindness, the lines on the palms and feet, etc. But this, as well as skin colour, is the result of biological adaption to specific environmental factors in a particular area which have been affecting our species over a prolonged period of time. Our racial differences reflect episodes from the adaptation history of our species Homo sapiens sapiens - a species coming from a tight ecological niche, which has spread around the globe. Those differences do not occur only as the result of the biological ability to adapt, which is inherent to all species to one extent or another. The difference between us and the rest of the species is that only humans have the innate ability to change their environment according to their needs - a human settles in extreme cold and invents the igloo and the anorak; they settle in dry region- and invent the artificial irrigation. This human ability is directly related to language, which distinguishes us from all other living beings. It has also made long-distance migrations possible, including migrations to other continents, where people faced new challenges and a new need to adapt.
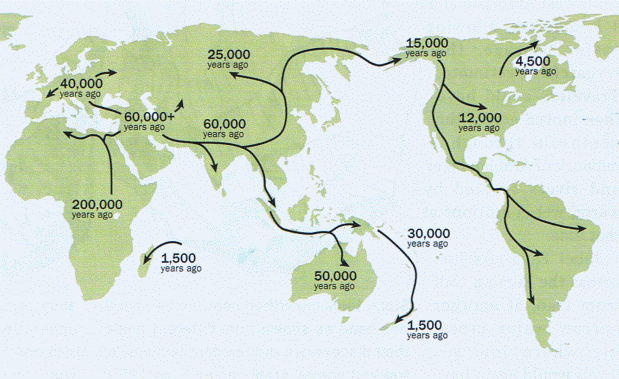
A map of man's migration through space and age
THE DNA FAIRYTALE
The evidence for these migrations can actually be found in our DNA.
It contains the history of our ancestors- those, whose direct descendants we are. We can find out which geographic region they came from, when and where they migrated, the layers of changes triggered by new environments, who they mixed with on the way. That is the story Mr. Joseph and Evgeny Delev learnt when they ran their DNA tests. In other words, they read the history of their families in particular. Evgeny says: "My African heritage is from the maternal side.
That was established after a study on the mitochondrial DNA, which is passed down from a mother to her children. That is how the direct maternal line can be traced back. In my case, it bears record that my distant great-grandmothers or at least one of them lived in Africa until around 12 000 years ago. More than 480 generations have passed since then. My numerous great-grandmothers mixed with many great-grandfathers. One carries genes from a large number of grandparents and shows in different degree different characteristics of theirs."
The colour of the skin, the hair, and the eyes depend on the pairing of the parents' genes. But the mitochondrial and the nuclear DNA, which contain the "record" for the geographic origin, do not take part in the recombination. Therefore, this record remains unchanged throughout the generations. Furthermore, it does not disappear and therefore it can be found in every member of the family- for the maternal and the paternal lines respectively. The two mechanisms of inheritance are different. Therefore, it is possible to be fair-skinned while also having a family line originating from Africa.
UNITED COLOURS
What will happen to the races? Taking into account the fact that the world is becoming more and more open and people are travelling and mixing more and more, probably at some point, although not soon, they will mix so much that the term "race" will be completely meaningless. According to Stephen Stearns- a professor in evolutionary biology at Yale University, characteristic features will gradually disappear and the population on Earth will become increasingly homogenous.
This will happen neither fast, nor everywhere. Where respective characteristics are the best response to the natural environment, they will be preserved. So, the differences will never disappear completely, but the average European, for example, will become darker. Blue eyes will be an even rarer exception, since the gene that is responsible for them is recessive and in order to have them, one has to have inherited a copy of this gene from each of their parents. The more the number of blue- eyed people decreases, the smaller the probability for them to meet and give birth to a child with sky-blue eyes. According to Stern, a good illustration of what people might look like in the future are the Brazilians; they are a mixture of Europeans, Africans and Native-Americans. In other words, we are heading towards united colours, as one of the promoters of the Human genome project joked.
* The example is given in Francis Collins' book "The language of life''.
Since 1993 he has been the head of an international team, whose purpose is to decode and map the human genome. He has also been the head of the institute, established with this purpose.
** James Watson, together with Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins, reveals the structure of the DNA, for which Watson received a Nobel Prize in 1962. Watson was the first head of the Human genome project
Wayne Joseph- a 51-year-old Afro-American is a highly respected member of his community. Although he has suffered because of his dark skin, he is still proud of his origin. He names his daughter Kenya. He brings up his children not to be ashamed of being Afro-American. And because of his keen interest in the history of his family and their ancestral home Africa, Mr. Joseph runs a DNA test in order to obtain more information about his family roots on the Black continent. The results amaze him. The test reveals a huge European heritage and 0% African one. Zero! It almost turns out, that Mr. Joseph is not black, despite of his skin color.*
THE BULGARIAN AFRICAN
Evgeny Delev is a physicist engineer, a Bulgarian immigrant who has settled comfortably in France. His hobby is genetic genealogy. He is conducting the so-called Bulgarian genetic project.
Its goal is to convince as many of our fellow-countrymen as possible to run a DNA test and to provide their personal information to a common data bank, in order for a detailed genetic profile of the Bulgarian nation to be formed. Evgeny is an attractive man with extremely white face and auburn hair. Of course, one of the first things he did at the start of the project was to send his own biological material for a DNA analysis. The result: on the maternal side he is a pure...African.
He belongs to a group typical for the Black continent, which besides there, can be seen in the Middle East, among some tribes on the Arabian Peninsula and, naturally, among Afro-Americans.
However, it is a rare exception in Europe- apart from Evgeny, there are only 4 or 5 such known cases. What is the explanation? How is it possible for a person with "European genes" to be black and a person with African ones- to be white? Why have the races "mixed up"?
A DROP OF BLOOD
The term "race" originated as an attempt to somehow classify people with visibly different physical features such as skin colour, eye shape, etc. Even at its beginnings, this term was loaded with prejudice, because to the physical differences, people attached various presumptions concerning the person's qualities and abilities. One of the first to have made an attempt for such a classification is the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the XVIII century. He divides the human kind into 4 continental subtypes- Europeans, Asians, Americans and Africans.
He wrote: "Europeans are keen of mind, noble, inventive, law-abiding citizens. Africans are sly, lazy, negligent, succumbing to the whims of their masters". Encouraged by such "science", humanity has witnessed colonial exploitation, Indian genocide, trade with African slaves, Nazi (and not only) racism, holocaust, apartheid, Ku-Klux-Klan, the murder of Martin Luther King and so on. Until not long ago, the rule about the "one drop of blood" was valid in the US. According to that rule, children born within the marriage of a white person with a coloured one were considered coloured, regardless of how much that drop of blood has been diluted over the generations. This rule had various negative implications. It all started from a single misconception, which first appeared at the end of XVIII century- that different races did not have a mutual ancestor, but that each had emerged and had evolved separately on its respective continent. Moreover, it was believed that they did so at a different pace and with different "success". Therefore, you see, some were better than others.
With the above-said we can more or less summarize this view, known as polygenism. Ever since the middle of XX century, no self-respecting scientist has supported this view. It was rooted out by the genetics discovery that the whole humanity shared a mutual and recent origin. Only the Chinese, up until recently, still argued that the yellow race had originated separately from the rest- from the so-called Peking Man- a local East-Asian version of the predecessor of Homo sapiens. DNA analysis of people from East Asia has proven otherwise. Asians, as well as everybody else, also originate from Africa.
The second misconception at the core of racism is that one's abilities are defined only by their genetic heritage and that whatever environment they might be in, they would still be who they were born to be. The discussion, whether genes or social conditions define one's abilities, has never fully abated, but instead of furiously confronting each other, scientists are starting to agree more and more that both factors have to be taken into count in correlation instead of opposition.

The direct maternal line of Evgeny Delev proves, that round 12 000 years ago a greatgrandmother of his had lived in Africa
GENES DO NOT MAKE THE RACE
From the point of view of genetics, the term race is void of meaning. People look differently, but not because genetically they are completely different. It is exactly the opposite - we extremely similar, the degree of similarity between all human creatures on the planet is 99.9%.
We are the most unified species on the planet. In all other species the inter-species variety is much higher; even in the species closest to us - the chimpanzee; it is 3 times bigger than that of people.
Regardless of which race two people belong to, their DNA subsequence is 99.6% identical. The "Human genome" project came to the following conclusions regarding races:
1. Within members of a race, different from ours, we can always find an individual with whom we have a higher genetic similarity, than with someone from our race. 2. The genetic variations within a single race are much greater those between races. 3. Within the framework of one race there are some common genetic patterns. But there is no pattern, which is present in every single member of that group; there are also none that cannot be observed in representatives of another race. Furthermore, as James Watson wrote in his remarkable book "DNA- the secret of life", 98% of our variations fall in the section of the genome where they have no effect.
Moreover, since natural selection eliminates mutations which affect the functions of important parts of the genome extremely efficiently..., variations mostly accumulate in the non-coding sections. The differences between us are small, and the differences which those differences lead to, are even more inconsequential." The above-said leads to the conclusion that cannot be separated into races based on their genes. According to contemporary science, our apparent physical differences, which we call racial, are a relatively small number; they are also superficial as they are result from insignificant genetic factors. Furthermore, these factors in no way influence intelligence, talents or character.
BLOOD BROTHERS
We have already stated that as a species, people are surprisingly similar. That is because our common ancestor lived in Africa. From this point of view we are all African. Furthermore, he lived relatively soon- around 150 000 years ago. These 1500 centuries are a mere blink of the eye from the point of view of evolution- extremely insufficient, for many significant mutations to take place and for the human population to "break down" to different subspecies. We are all Homo sapiens sapiens regardless of our skin colour.
Then why do we look so different?
It is obvious that a black and a white person do not look alike. The difference is mostly on the outside- if they could 'take off' their skin, there would be no way for you to tell who was who. Other information is also needed.
THE NAKED MONKEY
Skin colour is the most apparent difference. But before we take a closer look at it, let us rewind evolution until the moment when the first human line separated from the one of the anthropoid apes. This took place 5 million years ago. For all this time, the accumulated difference in the DNA between the human and the chimpanzee- our evolutionarily closest relative, is only 1 %. If you shaved a chimpanzee, you would see that its skin is white. But the chimp is not bare-skinned; it has a thick dark fur, which, apart from other functions, protects it from the ultraviolet rays of the strong sunlight in the areas it populates. There is an interesting theory why, given the fact that we are so close with chimps, they are hairy, and we are not.
The human evolves as a species in an era much hotter than the current one.
The chimpanzee is a forest animal while the human first evolves in the savannah, where they cannot escape from the heat in the shades between trees. A thinner fur means easier cooling of the body. Therefore, the less hairy ancient humans were probably also healthier. Also, the more naked females were perceived as more attractive by the males and therefore had more children, thus passing on the "naked" gene to the next generations. The British zoologist Desmond Morris, who describes our species as a zoological phenomenon, calls the human a "naked monkey"; according to him, nudity is the most distinctive feature, which distinguishes us from all other primates. A light skin without fur is, however, very vulnerable to the harmful ultraviolet radiation of the Sun. Everybody who has had severe sunburn on the beach knows that. The harmful effects of the ultraviolet radiation are mitigated by melanin- a colouring pigment, produced in the skin. The genetic mutation, which led to an increased production of that pigment, has secured the survival of its carriers.
With time, this mutation became dominant in the human population inhabiting East Africa.

CAFE AU LAIT
However, around 80-60 000 years ago people started migrating. Some settled in Equatorial Africa, where the Sun is even stronger, and therefore their skin became darker. Even today the people who live there have the darkest skin. Others left the continent and headed towards South Asia and Australia.
In South India, where the Sun is still beating down rather hard, the skin remained dark- not completely black, but rather a shade of "cafe au lait".
But in the north it gets lighter and lighter. As to the ones who settled in Europe, their skin became completely white, because there the sun is weaker, and accordingly, so are the ultraviolet rays. Yet, they are necessary for the synthesizing of vitamin D, which is formed in the skin and is essential for calcium absorption. It is crucially important because it guarantees strong bones. Its chronic deficit leads to heavy skeleton deformations. In women, they can be so severe that they could render normal birth impossible. To put it in simply - you do not have Vitamin D, you do not have calcium and you do not have children. In order for the skin to be more permeable to the scarce sunlight, the melanin in it should be less, i.e. the skin should be lighter. This is how having a lighter skin tone ensures better survival chances in areas with limited sunlight. Why are Inuit, who live so far in the north, dark-skinned hen? Because they have found another way to adapt to their environment in order to receive sufficient quantities of vitamin D- they eat mainly fish, which contains the vitamin in abundance.
Europeans are not an "upgraded version" of Africans. If a few white-skinned families and their fair-haired children settled in Africa for 100 000 years, natural selection would have enough time to do what it is supposed to. What would happen? Probably a part of the children would not survive, developing skin cancer. The rest would have a generation. A mutation would occur in some of their descendents, which would cause an increase in melanin levels in the skin and it would get darker, because it is "healthier". In this way after a sufficient number of years has passed, the children of their children would all be dark-skinned.
WHITE MEN CAN JUMP
Beside the fact that after people inhabited Europe they got whiter, their bodies changed as well. Why? In the heat of Africa, where the body should easily cool itself, there developed two body types with optimal ratio between skin surface and volume. The first one- the tall and skinny Maasai, are characterised by a constitution allowing body heat to be easily released. In the other one- the Pygmies, the body changed in such a way as to minimize energy expenditure when moving. They are hunters who are always on the run. In order to save energy their bodies got smaller; fewer calories were needed for their maintenance and they did not feel as heavy during the constant sprint under the beating sun. In the significantly colder Europe, which went through an Ice Age even after it was inhabited by people, the body should retain as much body heat as possible. Therefore, it became stockier with less skin surface, through which the heat could escape, and with a more massive bone system. Because of the differences in body structure, some claim that the best contestants in weight lifting are European, and the fastest athletes- African. But within each race there are various body constitutions.
Take the best high-jump athlete - the slender and long-legged Stefka Kostadinova, for example. Who says that white people cannot jump? Races differ in teeth structure, serum proteins, the percentage distribution of blood groups, type of colour-blindness, the lines on the palms and feet, etc. But this, as well as skin colour, is the result of biological adaption to specific environmental factors in a particular area which have been affecting our species over a prolonged period of time. Our racial differences reflect episodes from the adaptation history of our species Homo sapiens sapiens - a species coming from a tight ecological niche, which has spread around the globe. Those differences do not occur only as the result of the biological ability to adapt, which is inherent to all species to one extent or another. The difference between us and the rest of the species is that only humans have the innate ability to change their environment according to their needs - a human settles in extreme cold and invents the igloo and the anorak; they settle in dry region- and invent the artificial irrigation. This human ability is directly related to language, which distinguishes us from all other living beings. It has also made long-distance migrations possible, including migrations to other continents, where people faced new challenges and a new need to adapt.

A map of man's migration through space and age
THE DNA FAIRYTALE
The evidence for these migrations can actually be found in our DNA.
It contains the history of our ancestors- those, whose direct descendants we are. We can find out which geographic region they came from, when and where they migrated, the layers of changes triggered by new environments, who they mixed with on the way. That is the story Mr. Joseph and Evgeny Delev learnt when they ran their DNA tests. In other words, they read the history of their families in particular. Evgeny says: "My African heritage is from the maternal side.
That was established after a study on the mitochondrial DNA, which is passed down from a mother to her children. That is how the direct maternal line can be traced back. In my case, it bears record that my distant great-grandmothers or at least one of them lived in Africa until around 12 000 years ago. More than 480 generations have passed since then. My numerous great-grandmothers mixed with many great-grandfathers. One carries genes from a large number of grandparents and shows in different degree different characteristics of theirs."
The colour of the skin, the hair, and the eyes depend on the pairing of the parents' genes. But the mitochondrial and the nuclear DNA, which contain the "record" for the geographic origin, do not take part in the recombination. Therefore, this record remains unchanged throughout the generations. Furthermore, it does not disappear and therefore it can be found in every member of the family- for the maternal and the paternal lines respectively. The two mechanisms of inheritance are different. Therefore, it is possible to be fair-skinned while also having a family line originating from Africa.
UNITED COLOURS
What will happen to the races? Taking into account the fact that the world is becoming more and more open and people are travelling and mixing more and more, probably at some point, although not soon, they will mix so much that the term "race" will be completely meaningless. According to Stephen Stearns- a professor in evolutionary biology at Yale University, characteristic features will gradually disappear and the population on Earth will become increasingly homogenous.
This will happen neither fast, nor everywhere. Where respective characteristics are the best response to the natural environment, they will be preserved. So, the differences will never disappear completely, but the average European, for example, will become darker. Blue eyes will be an even rarer exception, since the gene that is responsible for them is recessive and in order to have them, one has to have inherited a copy of this gene from each of their parents. The more the number of blue- eyed people decreases, the smaller the probability for them to meet and give birth to a child with sky-blue eyes. According to Stern, a good illustration of what people might look like in the future are the Brazilians; they are a mixture of Europeans, Africans and Native-Americans. In other words, we are heading towards united colours, as one of the promoters of the Human genome project joked.
* The example is given in Francis Collins' book "The language of life''.
Since 1993 he has been the head of an international team, whose purpose is to decode and map the human genome. He has also been the head of the institute, established with this purpose.
** James Watson, together with Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins, reveals the structure of the DNA, for which Watson received a Nobel Prize in 1962. Watson was the first head of the Human genome project



